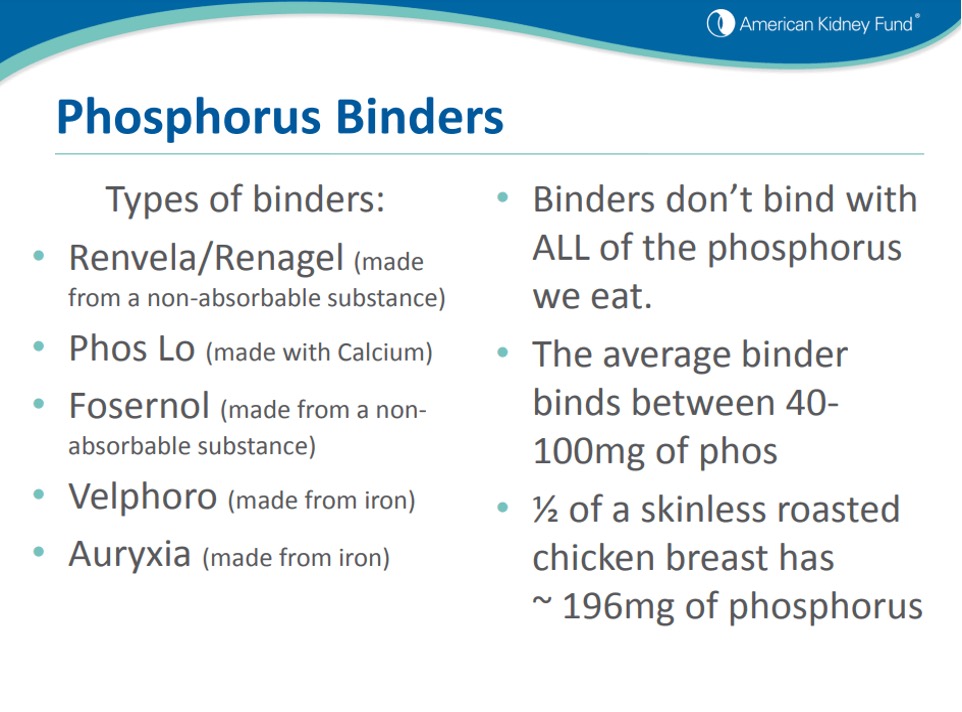
Phosphorus binders work by binding to phosphorus in the digestive tract, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream. This allows the excess phosphorus to be eliminated from the body through the feces. Phosphorus binders are typically taken with meals, as this is when most of the dietary phosphorus is absorbed.
There are several different types of phosphorus binders, including calcium-based binders, aluminum-based binders, non-calcium, and non-aluminum binders. The choice of binder will depend on a number of factors, including the individual’s kidney function, calcium levels, and other medical conditions. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate type and dosage of phosphorus binder.
Here are a few slides from the American Kidney Fund: